Brief History of Aptos Blockchain
Aptos was original called Diem, a blockchain project created by Facebook now Meta. It aims to solve the existing scalability issue as well provide full modularity of smart contract design that was not offered before.
Link to Whitepaper
Concept of Modules, Resources and Scripts
Modules can be seen as packages or libraries and they are created/belong-to atomically under a single account.
module 0xCAFE::your_contract_name {
// Beginning of your contract
}Generally, modules can be imported by other modules and live fully on-chain just like any other smart contracts.
Resource accounts expands the portability of the data that is being generated from the interaction with a module. They can represent any arbitrary data output, common ones include tokens or NFTs.
These accounts can be created by utilizing the functions from the native 0x1 library from Aptos.
Scripts are used to invoke functions in declared modules in addition to applying a set of logic by the caller.
script {
// Beginning of your script
}Scripts and Modules follow a similar code layout/format
Move, the Smart Contract Language on Aptos
One of the coolest thing that I have personally noticed is the idea of key rotation. This essentially allows the developer to change the signer of an account instead of creating an entirely new account or retrieve the signer of an existing module.
This brings so much flexibility to developers as they don’t have to keep creating new accounts or keep track of accounts that possess as a signer.
As an example, if an admin account for a module was compromised, the developer can quickly switch the signer of the module using a different account.
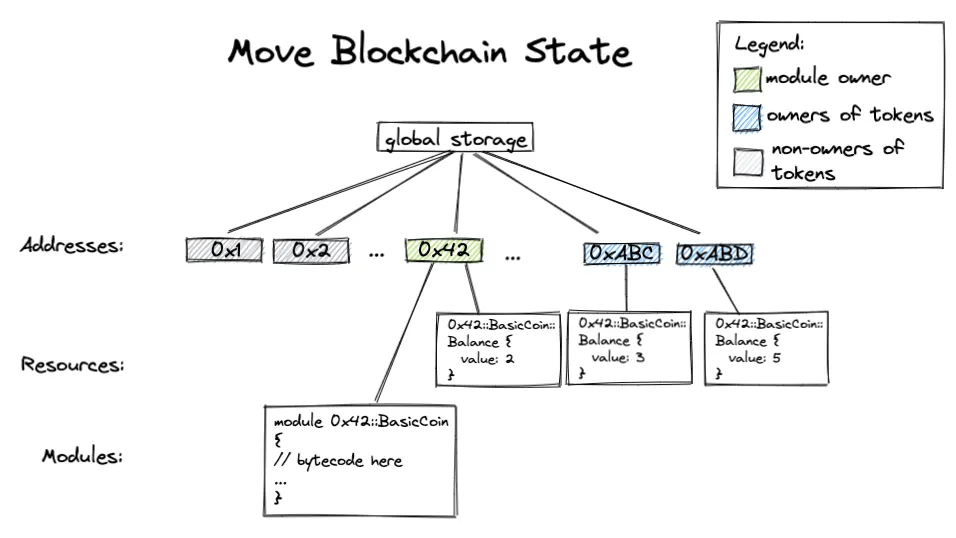
This is possible because the data is not directly tied to specific addresses but rather, they can be moved around different accounts since they are independent structures.
Data can be passed around by using specific operations for global storages which can be found here.
Random Move Facts
- Any imported modules have to be used. If not, the compiler will throw an error.
- Move compilers are just as smart as rust compilers, they are generally good at explaining errors.
- Move is very strict on its type and ownership system. As an example, make sure you read the function params carefully and always check if it wants the value directly or its reference.
- Arithmetic and comparison operations must be used between same integer types. If they are not, cast them to the same type!
- No need to use return keyword, the last expression will be returned by default.